Windows System
One of the main features that XRV offers is the Windows System, that helps you with built-in windows which contents can be customized by your own. It also includes built-in alert and confirmation dialogs, that you can include within your UI logic to notify or ask for confirmation to application users, and execute some logic or another based on their decisions.
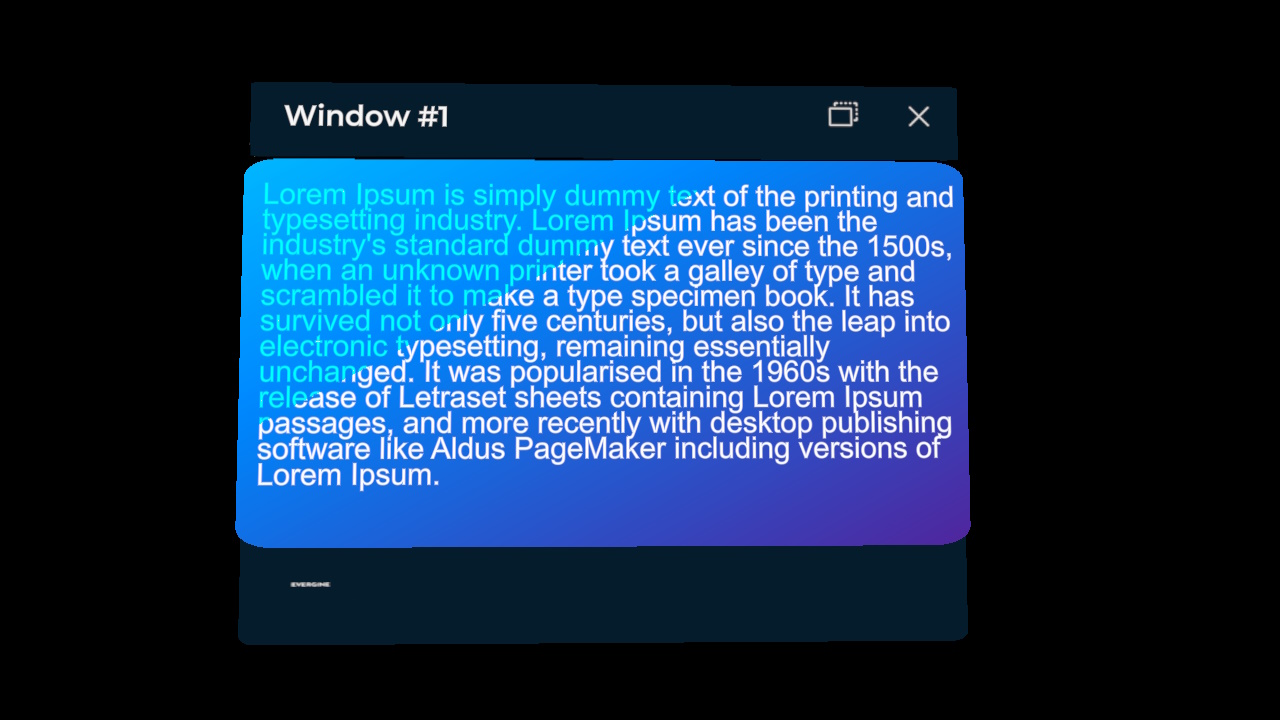
Windows interaction
When a window is created, it will include some default buttons that allows users to modify window behavior or visibility.
- Window position behavior can be changed, you can choose how window is placed relative to the user. To change position mode, just use window button to toggle between following behaviors:
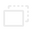 Follow mode: window will follow the user wherever he moves if he goes away by a distance higher than 0.6 meters. In this mode, window will also change its orientation to face the user if he moves around.
Follow mode: window will follow the user wherever he moves if he goes away by a distance higher than 0.6 meters. In this mode, window will also change its orientation to face the user if he moves around.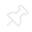 Pinned mode: when switched to this mode, window will stay in the position and orientation that button has when pressed. In this mode, user can also manipulate position and orientation of the window, using pinch gesture on surface area of the window, including both title bar and contents area.
Pinned mode: when switched to this mode, window will stay in the position and orientation that button has when pressed. In this mode, user can also manipulate position and orientation of the window, using pinch gesture on surface area of the window, including both title bar and contents area.
- Press
 to close the window.
to close the window.
Create and show a window programmatically
To create a window, you can do it accessing Windows System that is exposed by XrvService. This window creation have a callback to configure the window, with different options that we will enumerate in section below. You can create as many windows as you want.
var xrv = Application.Current.Container.Resolve<XrvService>();
var windowSystem = xrv.WindowSystem;
// Setting Window
var window = xrv.WindowSystem.CreateWindow(config =>
{
config.Title = "Window #1";
config.Size = new Vector2(0.3, 0.2);
});
// Show window (empty in this case)
window.Open();
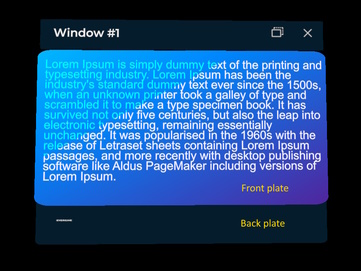
Windows include different built-in parts and layers:
- Title bar: this is on the top of the window, also contains action buttons on right side of the window.
- Back plate: it has the same material than title bar, and the unique content that it includes is an optional logo image.
- Front plate: it will be drawn over back plate, and is intended to be placed behind window contents.
Window instance options
Each window instance that is returned by Windows System offers a set of options that developers can change by their own criteria. You can also open or close any window programmatically or subscribe to events about that window being opened or closed.
| Properties | Description |
|---|---|
AllowPin |
If this option is disabled, default toggle button to let user change window positioning behavior that we commented above, will not be available for a window instance. |
DistanceKey |
This lets developers to specify the distance key that will be used to place window once opened. |
EnableManipulation |
When set to false, this option will not let users to change window orientation and positioning when pinned mode is active. |
| Methods | Description |
|---|---|
Open |
Opens window instance. |
Close |
Closes window instance. |
| Events | Description |
|---|---|
Opened |
It occurs when window instance is opened. |
Close |
It occurs when window instance is closed. |
Window instance configuration
On configuration callback, you can use following properties to change how window is displayed.
| Properties | Description |
|---|---|
Content |
This property lets you to set an entity that will be placed as window contents. Here you can set whatever you want: buttons, 3D text, images, etc. We will talk later about what is the easier way to layout your windows contents and how to set up window parameters like size to fits its contents. |
DisplayFrontPlate |
Front plate can be optionally hidden using this flag. |
DisplayBackPlate |
Back plate can be optionally hidden using this flag. |
DisplayLogo |
Controls logo visibility for the window. This image is located in bottom-left corner of the back plate. |
FrontPlateOffsets |
XY front plane offset relative to window back plate. |
FrontPlateSize |
Front plate width and height in meters. |
LocalizedTitle |
Lets you to specify callback function to set a localized title for the window. |
LogoMaterial |
To change default logo image, you can set your own material here. |
Size |
You can set window width and height in meters. |
Title |
Lets you to specify a fixed title string to your window. |
How-to: create own window with contents
If you want to create your own window, you should first know the size of its contents, but calculating this manually could be tricky. We are going to quickly explain the steps we follow in this case.
- Create a new scene, that will contain your window contents. Window contents will be then exported to a prefab that will be loaded as window contents.
- Create a new mesh with BorderlessFrontPlate material. This plane will be a help guide just to know how contents will fit in final window.
- Set PlaneMesh width and height with desired size.
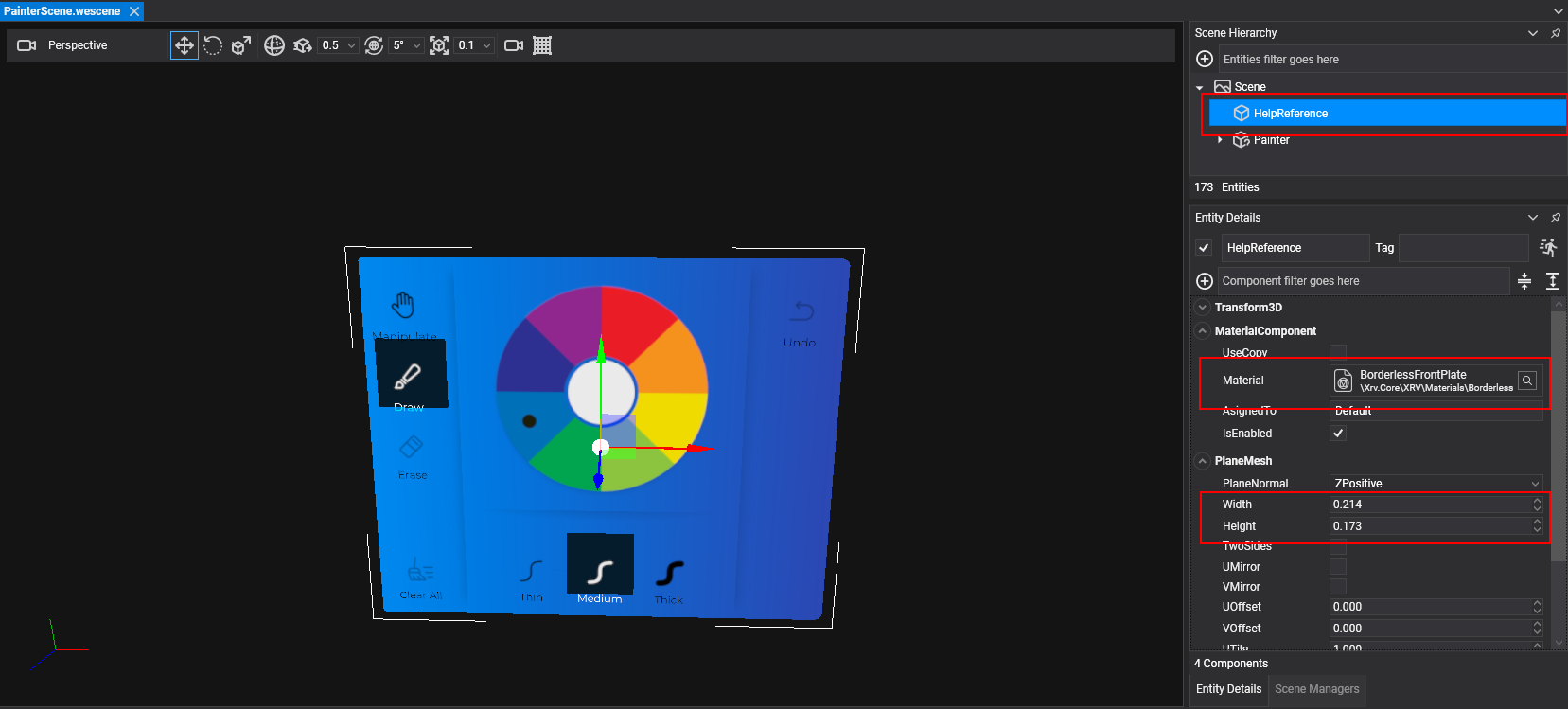
- Create your window layout.
- Create a prefab from your contents entity. Do not include guide reference in the prefab, just Painter entity in this case. Remember that you should not save your changes after creating the prefab.
- Instantiate your window from code, and set its size with same values as your reference.
var contentsSize = new Vector2(0.214f, 0.173f);
var window = windowsSystem.CreateWindow(config =>
{
config.Size = contentsSize;
config.FrontPlateSize = contentsSize;
config.Content = this.assetsService.Load<Prefab>(<Prefab GUID here>).Instantiate();
});
Built-in dialogs
XRV also offers two built-in dialog types that you can use to request a user action before making a decision. An important thing here is that, unlike windows creation, there could only be a single instance of alert or confirmation dialog at the same time in the application. We limit this to avoid dialog stacks that would make users uncomfortable while using the application.
- Alert dialog: this may be used to alert user about anything that happens while using the application, but where the user can choose no option, just confirm the dialog.
- Confirmation dialog: in this case, we can use this type of dialog to ask user for confirmation about an action, for example, removing a 3D model from virtual space.
Here you have an example of how use Windows System to show an alert or confirmation dialog.
var dialog = windowsSystem.ShowConfirmationDialog(...); // or ShowAlertDialog
dialog.Closed += Dialog_Closed;
private void Dialog_Closed(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
if (dialog is ConfirmDialog confirm)
{
dialog.Closed -= this.Dialog_Closed;
if (confirm.Result == confirm.AcceptOption.Key)
{
// Do something only if user taps on accept option
}
}
}
In the sample, you can notice that we are subscribing to Closed event. This is safe as long as you do event unsubscription in callback method, as we only allow a single dialog opened at the time. This means, if we have other part of the code that has already opened a dialog an is waiting for the response, this new dialog opening will provoke Closed event to be invoked for that previously executed code.
XRV dialogs have a property named Result that you can check to know which button has been pressed by the user.
Alert dialog
| Result value | It |
|---|---|
| AlertDialog.AcceptKey | When user presses dialog Accept button. |
| null | When user presses dialog Close button, or other part of the code invokes ShowAlertDialog. |
Confirmation dialog
| Result value | It |
|---|---|
| ConfirmationDialog.AcceptKey | When user presses dialog Accept button. |
| ConfirmationDialog.CancelKey | When user presses dialog Cancel button. |
| null | When user presses dialog Close button, or other part of the code invokes ShowConfirmationDialog. |
Other things that you can do with Windows System
Windows System instance also provide two properties that may be helpful for developers:
| Properties | Description |
|---|---|
Distances |
You can register or modify predefined window distances. |
OverrideIconMaterial |
This property allows to you to set a custom Material that will override default window logo material. So, you don't need to go instance by instance replacing default logo material. |
Window distances definition
XRV provides a set of predefined window distances, but you can add as many as you want to your application.
| Distance key | Value (in meters) | Usage |
|---|---|---|
NearKey |
0.35 | This is the distance used by default for alert and confirmation dialogs. |
MediumKey |
0.5 | This is the distance used by default for rest of the windows. |
FarKey |
1 | This is not used at all by built-in elements of XRV but you can use it by your own purpose. |
To override or add a new distance, you can use SetDistance method.
// override an existing key
windowsSystem.Distances.SetDistance(Xrv.Core.UI.Windows.Distances.NearKey, 0.45f);
// adding a new key
windowsSystem.Distances.SetDistance("custom", 0.5f);
// use distance key in a window
window.DistanceKey = "custom";
Examples
Get Windows System in component
public MyComponent : Component
{
[BindService]
private XrvService xrvService = null;
private windowSystem => xrvService.WindowSystem;
private void ShowAlert()
{
var dialog = this.windowSystem.ShowAlertDialog("Alert Title", "Sample Content.", "OK");
dialog.Closed += this.OnAlertClosed();
}
private void ShowConfirmation()
{
var dialog = this.windowSystem.ShowConfirmationDialog("Confirmation Title", "Sample Content.", "No", "Yes");
dialog.Closed += this.OnConfirmationClosed();
}
private void OnAlertClosed(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
if (sender is AlertDialog dialog)
{
dialog.Closed -= this.OnAlertClosed();
}
}
private void OnConfirmationClosed(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
if (sender is ConfirmationDialog dialog)
{
dialog.Closed -= this.OnConfirmationClosed();
}
}
}