Getting Started
Install Evergine.ImGUI extension
To start using this extension, just add Evergine.ImGui package to your project using NuGet package manager from Visual Studio.
<PackageReference Include="Evergine.ImGui" Version="2022.9.28.1" />
Register the ImGuiManager on your scene:
public class ImGuiSceneTest : Scene
{
public override void RegisterManagers()
{
base.RegisterManagers();
this.Managers.AddManager(new global::Evergine.Bullet.BulletPhysicManager3D());
this.Managers.AddManager(new ImGuiManager()
{
ImGuizmoEnabled = true,
ImPlotEnabled = true,
ImNodesEnabled = true,
});
}
...
}
And add the namespace ImGuiNET:
using ImGuiNET;
Now you can start calling the ImGui API from everywhere using the static reference:
private bool imguiDemoOpen;
...
ImguiNative.igShowDemoWindow(this.imguiDemoOpen.Pointer());
Usage
The UI is generated every frame and all the controls between Begin and End will be drawn.
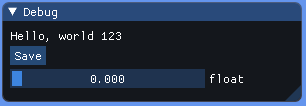
Here you have a simple example:
bool open = true;
ImguiNative.igBegin("Debug", open.Pointer(), ImGuiWindowFlags.None);
ImguiNative.igText("Hello, world 123");
if (ImguiNative.igButton("Save", Vector2.Zero))
{
// MySaveFunction();
}
float f = 0.5f;
ImguiNative.igSliderFloat("float", &f, 0.0f, 1.0f, null, ImGuiSliderFlags.None);
ImguiNative.igEnd();
And this is the result:
And now will see a more advanced example:
bool open = false;
ImguiNative.igBegin("Path Tracing", open.Pointer(), ImGuiWindowFlags.None);
float x = this.worldInfo.LightPosition.X;
float y = this.worldInfo.LightPosition.Y;
float z = this.worldInfo.LightPosition.Z;
ImguiNative.igSliderFloat("Camera Pos X", &x, -10.0f, 10.0f, null, ImGuiSliderFlags.None);
ImguiNative.igSliderFloat("Camera Pos Y", &y, -10.0f, 10.0f, null, ImGuiSliderFlags.None);
ImguiNative.igSliderFloat("Camera Pos Z", &z, -10.0f, 10.0f, null, ImGuiSliderFlags.None);
this.worldInfo.LightPosition.X = x;
this.worldInfo.LightPosition.Y = y;
this.worldInfo.LightPosition.Z = z;
float lightRadius = this.worldInfo.LightRadius;
ImguiNative.igSliderFloat("Light Radius", &lightRadius, 0.0f, 0.2f, null, ImGuiSliderFlags.None);
this.worldInfo.LightRadius = lightRadius;
int numRays = this.worldInfo.NumRays;
ImguiNative.igSliderInt("AO Num Rays", &numRays, 0, 32, null, ImGuiSliderFlags.None);
this.worldInfo.NumRays = numRays;
float aoRadius = this.worldInfo.AORadius;
ImguiNative.igSliderFloat("AO Radius", &aoRadius, 0.0f, 2.0f, null, ImGuiSliderFlags.None);
this.worldInfo.AORadius = aoRadius;
int numBounces = this.worldInfo.NumBounces;
ImguiNative.igSliderInt("GI Num Bounces", &numBounces, 0, 3, null, ImGuiSliderFlags.None);
this.worldInfo.NumBounces = numBounces;
float reflectanceCoef = this.worldInfo.ReflectanceCoef;
ImguiNative.igSliderFloat("Reflectance Coef", &reflectanceCoef, 0, 1, null, ImGuiSliderFlags.None);
this.worldInfo.ReflectanceCoef = reflectanceCoef;
float roughness = this.worldInfo.Roughness;
ImguiNative.igSliderFloat("Roughness", &roughness, 0,1, null, ImGuiSliderFlags.None);
this.worldInfo.Roughness = roughness;
ImguiNative.igSpacing();
ImguiNative.igSeparator();
ImguiNative.igSpacing();
int numSamples = this.pathTracerNumSamples;
ImguiNative.igSliderInt("Num Samples", &numSamples, 0, 1024, null, ImGuiSliderFlags.None);
this.pathTracerNumSamples = numSamples;
ImguiNative.igProgressBar((float)this.pathTracerSampleIndex / (float)this.pathTracerNumSamples, Vector2.Zero, null);
ImguiNative.igEnd();
This is the result:
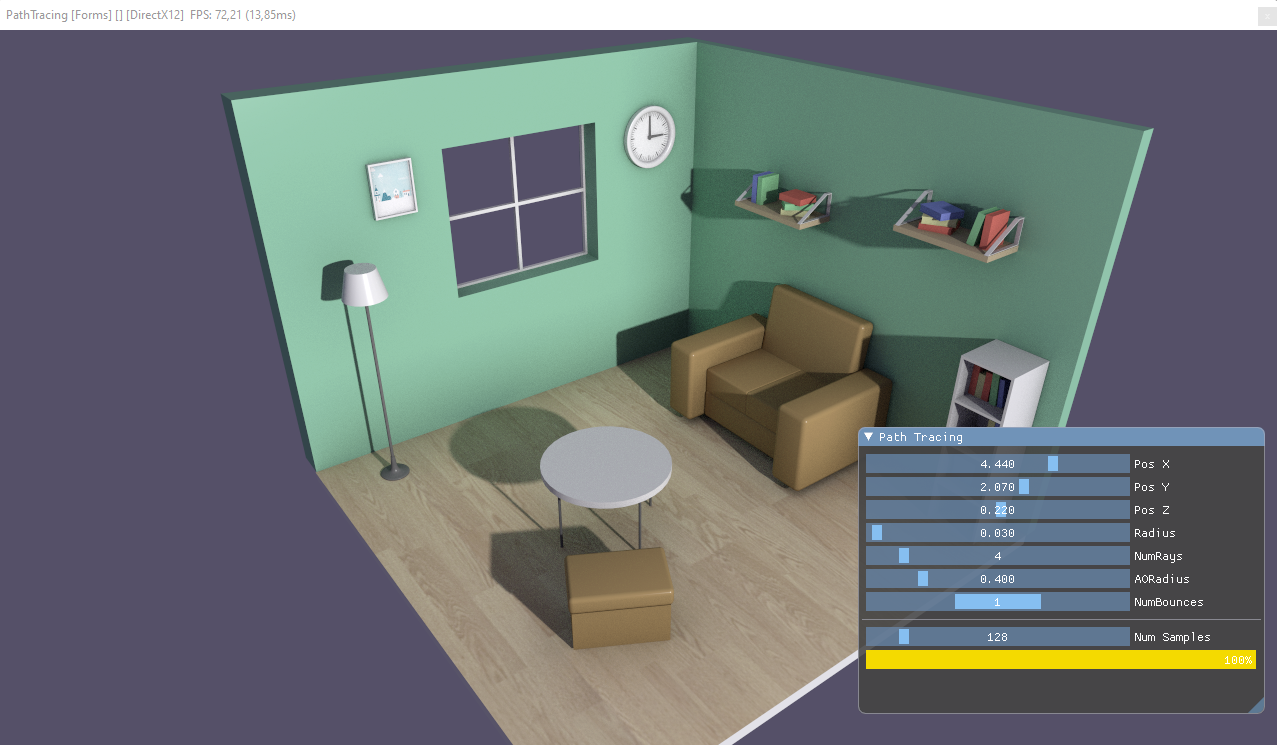
Take a look this in our path tracer demo.
Note: This project need to create a ImGuiRenderer because is using the Evergine low level api, but this is not necessary in a default project created from the Evergine Studio.