Physic Queries
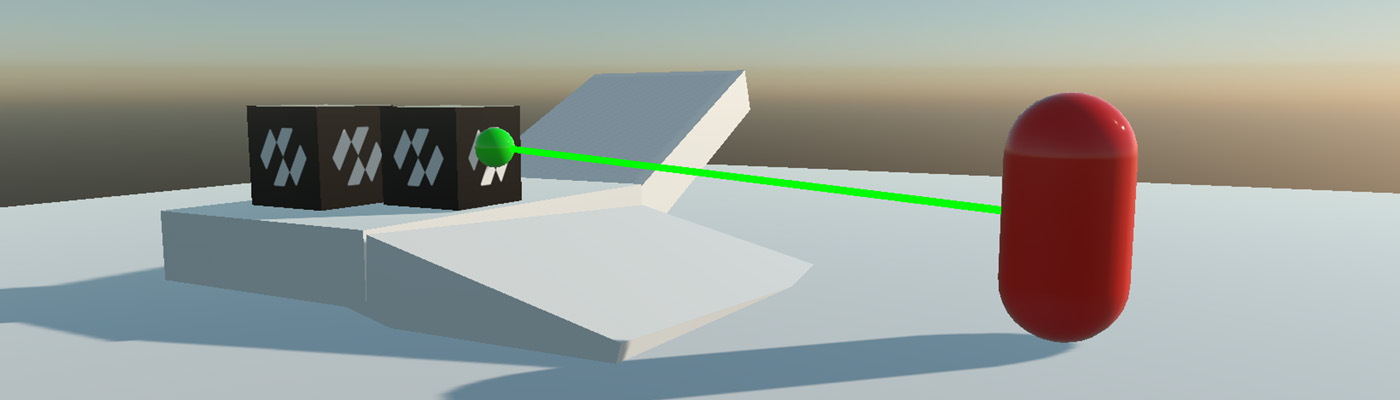
You can use physics Raycast queries to determine whether a specific line segment intersects physics geometry.
Similarly a SweepTest query tests whether a shape extruded along a line segment intersects with physics geometry. Example uses for these queries might include determining whether an object is in front of another object, or testing a line of sight.
Raycast
Raycast queries are the most common scene query, based on firing a ray from a start position a specified distance along a ray direction.
There are two ways to perform a raycast:
Closest Hit: Return the closest hit position detected by the raycast
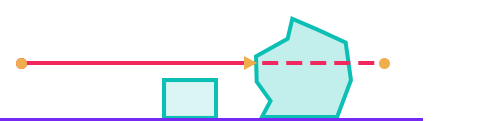
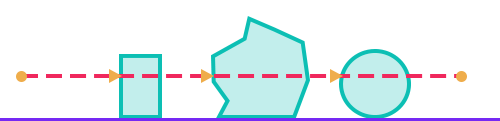
All Hits: Return all hits produced between the start and end position.
| Method | Description |
|---|---|
| Raycast(from, to, ...) | Perform a raycast between the specified from and to positions. Returns a HitResult3D instance with the result. |
| Raycast(ray, distance, ...) | Perform a raycast defined a Ray (position and direction) and a maximum distance. Returns a HitResult3D instance with the result. |
| RaycastAll(from, to, resultsOutput, ...) | Perform a raycast between the specified from and to positions. Returns all hits in a HitResult3D collection, which need to be passed as argument. |
| RaycastAll(ray, distance, resultsOutput, ...) | Perform a raycast defined a Ray (position and direction) and a maximum distance. Returns all hits in a HitResult3D collection, which need to be passed as argument. |
Using raycast from code
[BindComponent]
private Transform3D transform;
public float RayDistance {get; set;} = 10
private List<HitResult3D> hitCollection = new List<HitResult3D>();
protected override void Update(TimeSpan gameTime)
{
// Launch a raycast from the transform position, pointing to the transform forward...
var from = this.transform.Position;
var to = from + (this.transform.WorldTransform.Forward * this.RayDistance);
// Perform a hit test, getting the closest result...
var hitResult = this.Managers.PhysicManager3D.RayCast(ref from, ref to);
if (hitResult.Succeeded)
{
this.DebugHit(hitResult);
Console.WriteLine("Hit detected!");
}
// Perform a hit test, getting all results...
// Clear the previous hits..
this.hitCollection.Clear();
this.Managers.PhysicManager3D.RayCastAll(ref from, ref to, this.hitCollection);
foreach (var hit in this.hitCollection)
{
this.DebugHit(hit);
Console.WriteLine("Process hit!");
}
}
Sweep test
A Sweep test query is similar to a raycast query except that a sweep query takes a Collider as well as a point and direction. The collider shape is swept along the ray to form a volume. Anything that intersects with this volume is returned from the query.
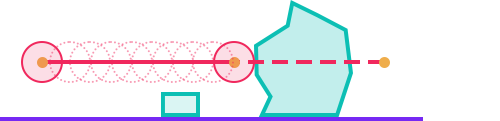
| Method | Description |
|---|---|
| ConvexSweepTest(colliderShape, from, to, ...) | Perform a sweep test between the specified from and to transforms (Matrix4x4 values, because you can specify position, orientation, scale). Returns a HitResult3D instance with first position in which the collider hit. |
| ConvexSweepTestAll(colliderShape, from, to, resultOutput, ...) | Perform a sweep test between the specified from and to transforms (Matrix4x4 values, because you can specify position, orientation, scale). Returns all hits in a HitResult3D collection, which need to be passed as argument. |
Using Sweep test from code
[BindComponent]
private Collider3D collider;
[BindComponent]
private Transform3D transform;
public float RayDistance {get; set;} = 10
private List<HitResult3D> hitCollection = new List<HitResult3D>();
protected override void Update(TimeSpan gameTime)
{
// Launch a sweeptest from the transform position, pointing to the transform forward...
var from = this.transform.WorldTransform;
var to = from * Matrix4x4.CreateTranslation(this.transform.WorldTransform.Forward * this.RayDistance);
// Perform a sweep test, getting the closest result...
var hitResult = this.Managers.PhysicManager3D.ConvexSweepTest(collider.InternalColliderShape,ref from, ref to);
if (hitResult.Succeeded)
{
this.DebugHit(hitResult);
Console.WriteLine("Hit detected!");
}
// Perform a sweep test, getting all results...
// Clear the previous hits..
this.hitCollection.Clear();
this.Managers.PhysicManager3D.ConvexSweepTestAll(collider.InternalColliderShape, ref from, ref to, this.hitCollection);
foreach (var hit in this.hitCollection)
{
this.DebugHit(hitResult);
Console.WriteLine("Process hit!");
}
}
HitResult3D
All physic queries use the HitResult3D structure to return all hit information. This structure contains all the required information to process a hit result:
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| Succeeded | Indicates if the query has successfully hit another object. |
| Point | The hit position in world space. |
| Normal | The hit normal vector. |
| HitFraction | A value between [0-1] indicating if the hit is produced in the start position 0, or at least end position 1 |
| PhysicBody | The hit physic body |
| Collider | The hit collider. You need to take in consideration that a physic body can have multiple colliders. |
| TriangleIndex | If the hit collider is a MeshCollider, specify the intersected triangle index in this mesh. |
Using HitResult3D from code
In the previous sample we used a DebugHit() method:
private void DebugHit(HitResult3D hitResult)
{
var lineBatch = this.Managers.RenderManager.LineBatch3D;
// Draw the hit position
lineBatch.DrawPoint(hitResult.Point, 0.2f, Color.Red);
// Draw the hit normal
lineBatch.DrawLine(hitResult.Point, hitResult.Point + (hitResult.Normal * 0.5f), Color.Yellow);
}