Pointers and Control
MRTK introduces new ways to interact with controls beyond the traditional mouse pointer, using hand-tracking features available on supported devices.
There are two main interaction methods:
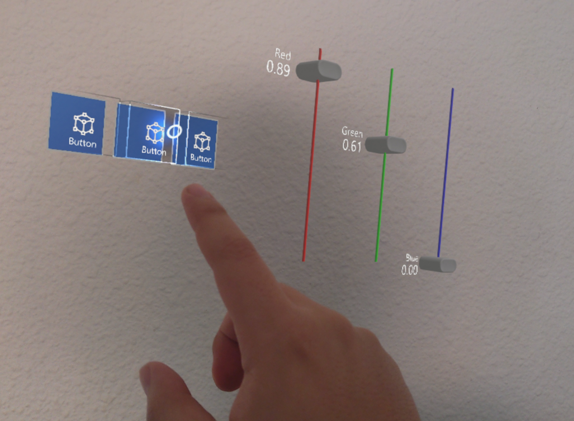
Near Interaction: When a user is close to a control, they can interact by touching it with their index finger. This is enabled by the near pointer mechanism.
Far Interaction: When the user is farther away but still wants to interact, they can use the far pointer. Through hand tracking, this appears as a light ray extending from their hand, which they can use to point and click. The gesture for clicking at a distance is known as an air-tap.
 |
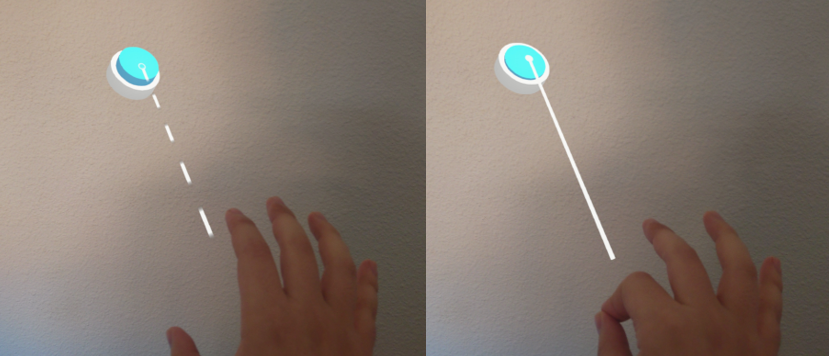 |
|---|---|
| Near Pointer Interaction Example | Far Pointer Interaction Example usage |
In devices that support hand-tracking, MRTK automatically creates the necessary pointers in the XRScene.
Desktop Development
These interaction methods are also available in desktop-based Evergine projects. The pointers can be controlled via the keyboard and mouse.
- Press and hold the left shift key to activate the right-hand pointer or the space key to activate the left-hand pointer. You can then move the pointer using the mouse.
- Use the mouse wheel to move the pointer closer to or farther from the camera.
- Use the left mouse button to perform the air-tap gesture, allowing interaction with distant controls.
- Press and hold the left control key to rotate the selected pointer using the mouse.