Create Audio from Code
In this section, the essential elements for reproducing audio in your project are explained in more detail.
Audio Device
An Audio Device is a class that represents an audio output device. Evergine supports two audio device implementations:
| Audio Device Implementation | Platforms Supported | Description |
|---|---|---|
| XAudioDevice | Windows, Hololens | A lower-level audio API for Microsoft Windows, Xbox 360, and Windows Phone 8. It is the successor to DirectSound on Windows and a supplement to the original XAudio on the Xbox 360. |
| ALAudioDevice | Windows, Web, Android, IOS, Linux, Mac | A cross-platform audio application programming interface (API) designed for efficient rendering of multichannel three-dimensional positional audio. Its API style and conventions deliberately resemble those of OpenGL. OpenAL is an environmental 3D audio library that can add realism to a game by simulating attenuation (degradation of sound over distance), the Doppler effect (change in frequency as a result of motion), and material densities. OpenAL was originally intended to be an open standard and open-source replacement for proprietary (and generally incompatible) 3D audio APIs such as DirectSound and Core Audio, though in practice it has largely been implemented on various platforms as a wrapper around said proprietary APIs or as a proprietary and vendor-specific fork. |
In the Program.cs class in the Evergine project template, it is possible to see the implementation used as an Audio Device:
Creating a XAudio2 Implementation
// Creates XAudio device
var xaudio = new global::Evergine.XAudio2.XAudioDevice();
application.Container.RegisterInstance(xaudio);
Creating an OpenAL Implementation
// Creates OpenAL device
var audioDevice = new Evergine.OpenAL.ALAudioDevice();
application.Container.RegisterInstance(audioDevice);
Its most relevant methods are:
| Method | Description |
|---|---|
| CreateAudioSource | Creates an audio source where you can enqueue audio buffers. |
| CreateAudioBuffer | Creates an audio buffer. |
Audio Buffer
An Audio Buffer represents a sound. When you drag an audio file into Evergine Studio, an audio asset is created automatically. You can load an AudioBuffer from an audio asset using the AssetService:
// Create audioBuffer from audio asset.
AudioBuffer audioBuffer = assetsService.Load<AudioBuffer>(EvergineContent.Audio.sound1_wav);
It is also possible to create an audio buffer with procedural data:
// Create buffer
this.format = new WaveFormat(false);
this.buffer = this.AudioDevice.CreateAudioBuffer();
// Fill with data
var bufferData = new byte[100 * this.format.BlockAlign];
this.buffer.Fill(bufferData, 0, bufferData.Length, this.format);
For more details, see the AudioBuffer API reference.
Audio Source
An Audio Source represents the audio queue where it is possible to enqueue several audio buffers and reproduce them one after another.
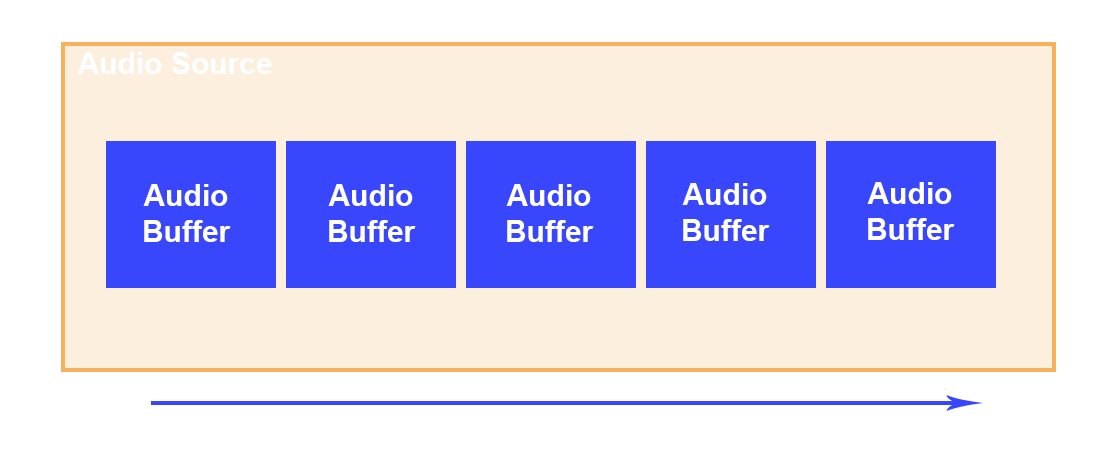
To enqueue an audio buffer and play it:
// Load audio buffer
AudioBuffer audioBuffer = assetsService.Load<AudioBuffer>(EvergineContent.Audio.sound1_wav);
// Get Audio Device instance
AudioDevice audioDevice = Application.Current.Container.Resolve<AudioDevice>();
// Create Audio Source
AudioSource audioSource = audioDevice.CreateAudioSource(audioBuffer.Format);
// Enqueue audio buffer
if (audioSource.PendingBufferCount == 0)
{
audioSource.EnqueueBuffer(audioBuffer);
}
// Play the audio source.
audioSource.Play();
Its most relevant methods are:
| Method | Description |
|---|---|
| EnqueueBuffer | Enqueues an audio buffer. |
| Play | Plays all buffers enqueued in the audio source. |
| Pause | Pauses the audio source reproduction. |
| Stop | Stops the audio source reproduction. |
For more details, see the AudioSource API reference.