Tonemapping, Chromatic Aberration, Vignette, Grain, Distortion
In this section, multiple effects are explained because the process steps to calculate them are similar and they were implemented together for performance reasons.
Tonemapping
Tonemapping is a technique used in image processing and computer graphics to map one set of colors to another to approximate the appearance of high-dynamic-range images in a medium that has a more limited dynamic range.
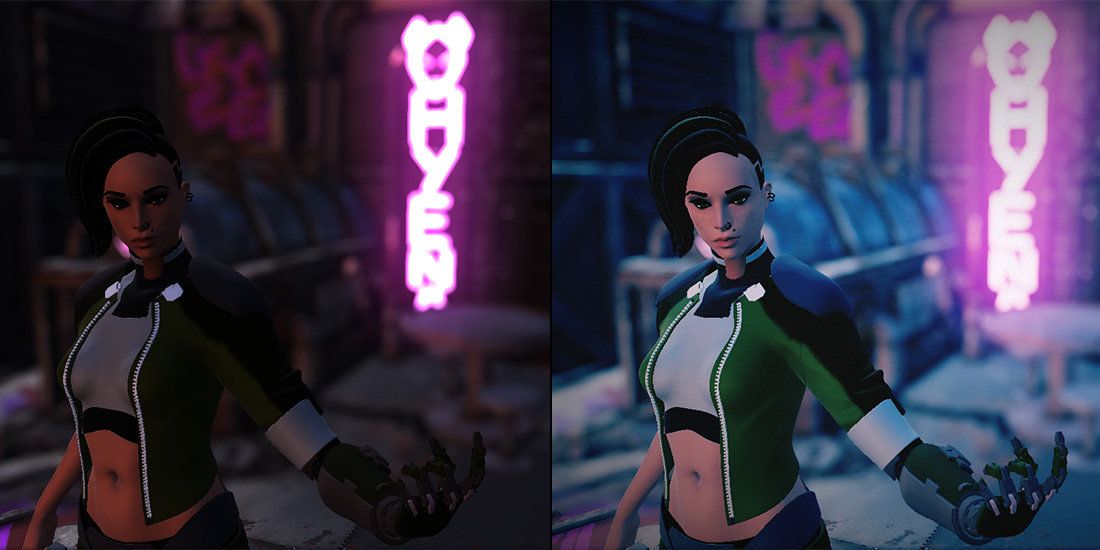

In the above image, the left side is the render without tonemapping applied, and the right side is the result of applying tonemapping to the left side.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| HDR Enabled | Enables/Disables mapping of High Dynamic Range (HDR) to Low Dynamic Range (LDR). |
| Curve | Defines how to map the image color to the output image. The following curves are available: Reinhard, ReinhardSQ, LumaReinhard, Filmic, ACES, RombindAHouse. The default curve is ACES. |
| LUT Enable | Enables/Disables the use of the Lookup Table (LUT) texture to map the colors. |
| LUT Texture | Represents a Lookup Table (LUT) 16x16x16 color neutral unwrapped to a 256x16 texture. There are two LUT Texture samples: HDR:  Vintage:  |
Chromatic Aberration
Chromatic aberration, also known as “color fringing” or “purple fringing,” is a common optical problem that occurs when a lens is either unable to bring all wavelengths of color to the same focal plane, and/or when wavelengths of color are focused at different positions in the focal plane. Chromatic aberration is caused by lens dispersion, with different colors of light traveling at different speeds while passing through a lens. As a result, the image can look blurred or noticeable colored edges (red, green, blue, yellow, purple, magenta) can appear around objects, especially in high-contrast situations.
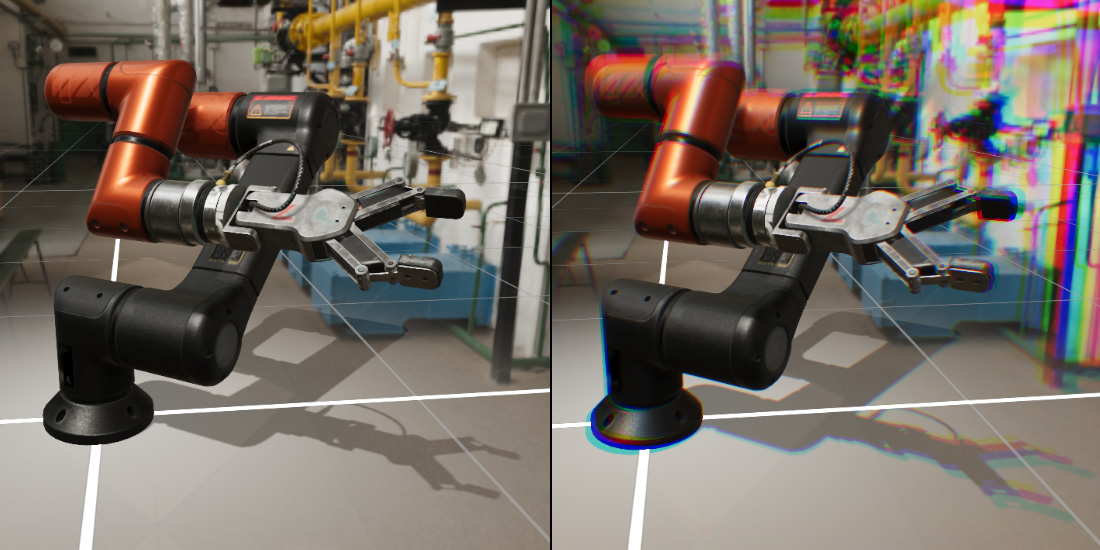
In the above image, the left side is the render without chromatic aberration applied, and the right side is the result of applying chromatic aberration to the left side.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Strength | Defines the distance between color bands. |
| Offset | Defines the vector direction of the aberration. |
Grain
If you’ve watched a film and seen speckles on the screen in random patterns, you’ve seen film grain. Originally, the actual grains in film grain were small particles of silver halide, the primary photosensitive substance used in chemical film. These particles are randomly distributed artifacts throughout the image.
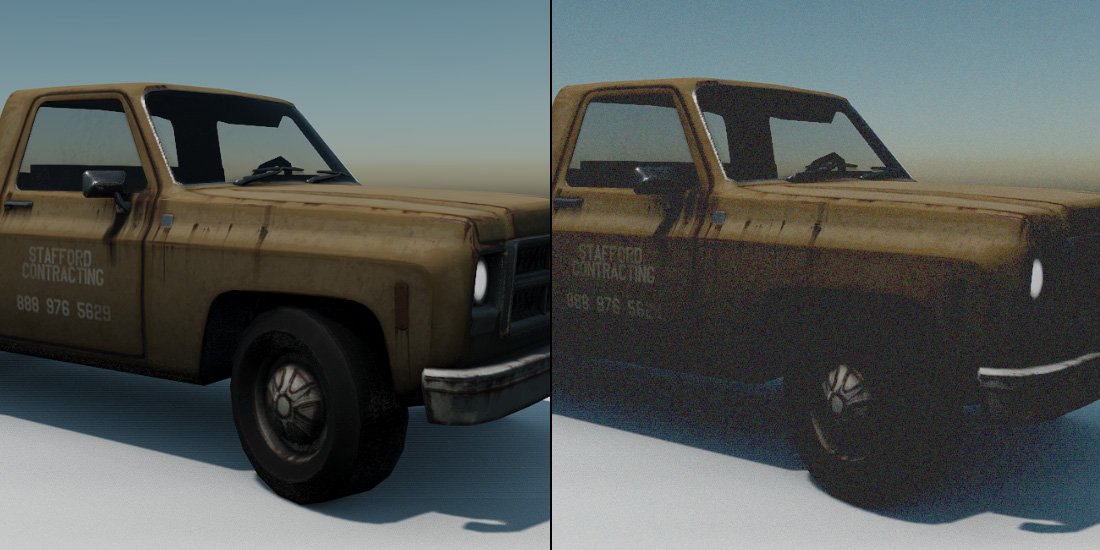

| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Intensity | Defines the intensity of the grain effect. |
Vignette
A vignette is a decrease in brightness of a photograph towards its edges compared to the image center. Vignetting is often an undesired effect caused by camera settings that are not suitable for the given light situation. However, the effect can also be added subsequently to create noticeable changes in the picture’s mood and perception by making subtle changes.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Power | Defines the intensity of the vignette effect. |
| Ratio | Defines the ratio of the effect with respect to the center of the image. |
Distortion
This is a visual effect that simulates the effect produced by the refraction of light. Examples of this effect include looking through glass or fire smoke.
Tip
This effect requires the use of the Distortion Material included in the Evergine.core package.
