Rigid Bodies

Rigid bodies are moved around by forces such as collisions and gravity. In general, rigid bodies are a good choice for objects that can be moved or pushed, like boxes, furniture, and obstacles.
In Evergine, we use the RigidBody3D component to provide the functionality required to turn an Entity into a rigid body.
Every frame, the PhysicManager updates the state of every registered rigid body, changing their poses and detecting collisions.
RigidBody3D Component
In Evergine, we use the RigidBody3D component to provide the functionality required to turn an Entity into a rigid body.
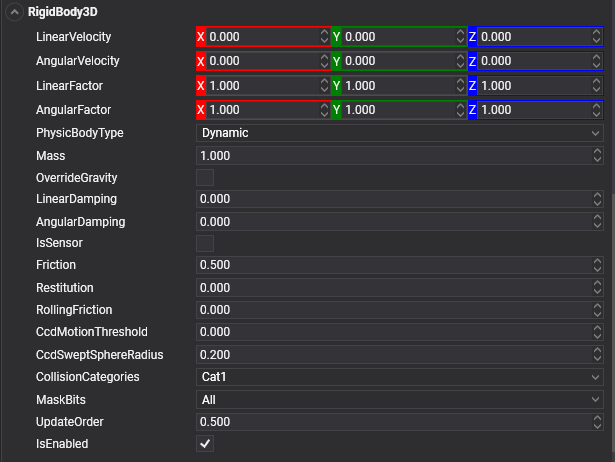
General Properties
| Property | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Mass | 1.0 | Sets the mass of the rigid body. Try to avoid large mass ratios (differences). |
| Restitution | 0 | Sets the amount of kinetic energy lost or gained after a collision. A typical value is between 0 and 1. If the restitution property of colliding bodies is 0, the bodies lose all energy and stop moving immediately on impact. If the restitution is 1, they lose no energy and rebound with the same velocity they collided at. Use this to change the "bounciness" of rigid bodies. |
| Friction | 0.5 | Sets the surface friction. |
| RollingFriction | 0 | Sets the rolling friction. |
| CollisionCategory | Cat1 |
The CollisionCategory flag specifies the category of this body. |
| MaskBit | All |
The MaskBits indicate with which categories this body will collide. |
Motion Properties
The following properties affect the movement of the rigid body.
| Property | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|
| LinearVelocity | 0,0,0 | Sets the initial linear velocity. |
| LinearFactor | 1,1,1 | This property is used to limit the translation of a rigid body. It's separated into X, Y, and Z. If one of these axes is set to 1, the movement is not limited, and if a value is set to 0, the axis is locked. |
| LinearDamping | 0 | Used to slow down the movement of an object. The higher the drag, the more the object slows down. |
| AngularVelocity | 0,0,0 | Sets the initial angular velocity. |
| AngularFactor | 1,1,1 | This property is used to limit the rotation of a rigid body. It's separated into X, Y, and Z. If one of these axes is set to 1, the rotation is not limited, and if a value is set to 0, the axis is locked. |
| AngularDamping | 0 | Used to slow down the rotation of an object. The higher the drag, the more the rotation slows down. |
| OverrideGravity | false | Indicates if this rigid body will define its own gravity value instead of using the common value defined in PhysicManager. |
| Gravity | 0,-9.8,0 | If OverrideGravity is true, the rigid body will use this value as the gravity intensity. |
| IsSensor | false | If you set a physics body to be a sensor, other colliders no longer bump into it. Instead, they pass through. Sensors detect when bodies enter it, which you can use in your application. |
Kinematic Rigid Bodies
There are two types of rigid bodies: dynamic and kinematic bodies.
In Dynamic rigid bodies, their movement is driven by the physics simulation. They receive forces and can be pushed by other bodies.
In contrast, Kinematic rigid bodies are not influenced by forces (such as gravity) and have no momentum. They cannot be pushed by other rigid bodies, and their movement is only controlled by changing their transform. An elevator platform is a good example of a kinematic rigid body.
Although kinematic rigid bodies aren't moved by physics, other objects can still collide with them. For example, in the case of an elevator, objects placed inside won't fall through the elevator floor.
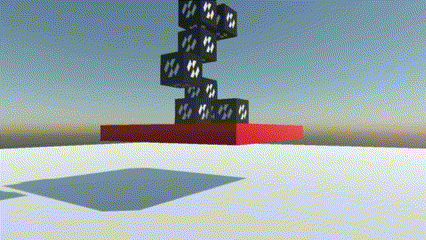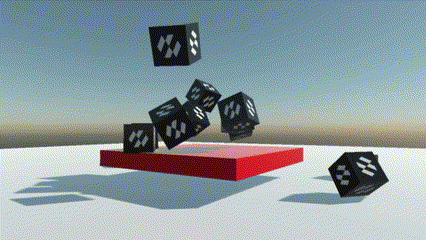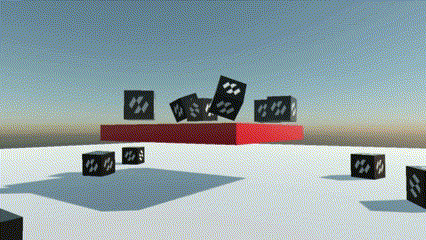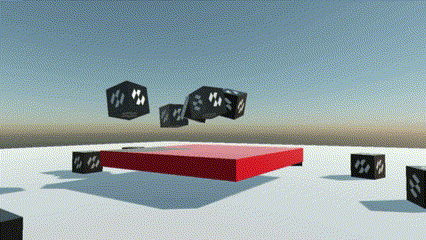
It is possible to specify the type of rigid body with the PhysicBodyType property:
| Property | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|
| PhysicBodyType | Dynamic | There are two types of rigid bodies:
|
Create a RigidBody
You only need to add a RigidBody3D to an entity to turn it into a rigid body. Don't forget to add a proper collider too.
From Code
A small example to create a bouncing sphere:
Entity bouncingBall = new Entity()
.AddComponent(new Transform3D() { Position = position })
.AddComponent(new MaterialComponent() { Material = material }) // Assign a material
.AddComponent(new SphereMesh())
.AddComponent(new MeshRenderer())
.AddComponent(new RigidBody3D() // Add a RigidBody3D component...
{
Restitution = 1.0f // Create a bouncing ball (restitution 1)
})
.AddComponent(new SphereCollider3D()); // Assign a SphereCollider3D to the physics body...
this.Managers.EntityManager.Add(bouncingBall);