Using Scenes
To load and launch a Scene from code, we need to use ScreenContextManager and understand the concept of ScreenContexts.
ScreenContext
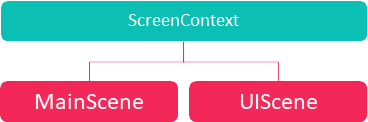
A ScreenContext represents a list of Scenes that can be simultaneously loaded in the application.
Note
For example, the diagram above depicts a ScreenContext containing two scenes: MainScene for the application logic and UIScene, another one just for the UI.
ScreenContextManager
ScreenContextManager is a Service that manages the Scene navigation between scenes or, more accurately, ScreenContexts. Its main methods are:
| Method | Description |
|---|---|
| To | Navigates to a new ScreenContext (passed by parameter), replacing the previous ScreenContext. |
| Push | Navigates to a new ScreenContext but keeps the previous one in a stack so we can restore it later. |
| Pop | Removes the current ScreenContext and restores the previous stacked one. |
| FindContextByName | Searches among the ScreenContext list. |
So, loading and navigating to a Scene by code would be like this (this code is placed in the Application class):
// Loads the scenes. This will create MyScene and UIScene objects which should be existing classes that inherit from the Scene class.
// These scenes are populated with all entities defined in their respective assets (MainScene.wescene and UIScene.wescene).
var baseScene = assetsService.Load<MyScene>(EvergineContent.Scenes.MainScene_wescene);
var uiScene = assetsService.Load<UIScene>(EvergineContent.Scenes.UIScene_wescene);
// Creates a context and navigates to it.
ScreenContext screenContext = new ScreenContext(baseScene, uiScene);
screenContextManager.To(screenContext);
For more details, read the ScreenContextManager section.