Generic 6DoF Joint
The Generic 6DoF Joint can emulate a variety of standard constraints if each of the six Degrees of Freedom (DoF) is configured. The first 3 DoF axes are linear axes, representing the translation of rigid bodies, while the latter 3 DoF axes represent the angular motion. Each axis can be locked, free, or limited. By default, all axes are unlocked.
Generic6DoFJoint3D
In Evergine, a Generic 6DoF Joint is implemented using the Generic6DoFJoint3D component.
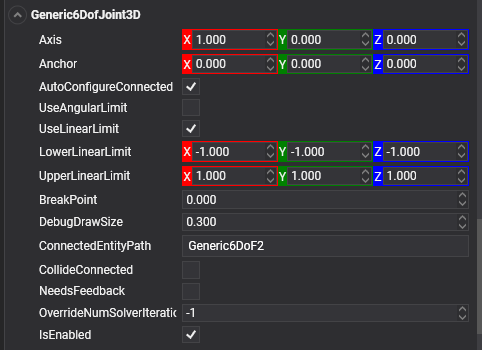
Properties
Common Properties
| Property | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|
| ConnectedEntityPath | null | The entity path of the connected body. Only when the path is valid is a joint established properly. |
| Anchor | 0, 0, 0 | The point that defines the center of the joint in the source entity's local space. All physics-based simulations use this point as the center in calculations. |
| AutoConfigureConnected | true | Enable this setting to automatically calculate the ConnectedAnchor position to match the global position of the anchor property. This is the default setting. Disable it to configure the position of the connected anchor manually. |
| ConnectedAnchor | auto-calculated | Manually configure the connected anchor position in the connected body's local space. |
| BreakPoint | 0 | If the value is greater than 0, it indicates the force that needs to be applied for this joint to break. |
| CollideConnected | false | Determines whether a collision between the two bodies managed by the joint is enabled. |
Limit Properties
The following properties set the limits of the object's movement.
| Property | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|
| UseLinearLimit | false | If enabled, the position of the connected object will be restricted within the LowerAngularLimit & UpperAngularLimit values. |
| LowerLinearLimit | 0 | The lower distance of the limit. |
| UpperLinearLimit | 0 | The upper distance of the limit. |
| UseAngularLimit | false | If enabled, the angular rotations will be restricted within the LowerAngularLimit & UpperAngularLimit values. |
| LowerAngularLimit | 0 | The lowest angle the rotation can go. |
| UpperAngularLimit | 0 | The highest angle the rotation can go. |
Using Generic 6DoF Joint
This snippet uses a Generic6DoF to replicate the same functionality shown in the Slider Joint example.
protected override void CreateScene()
{
this.Managers.RenderManager.DebugLines = true;
// Load your material
var material = this.Managers.AssetSceneManager.Load<Material>(DefaultResourcesIDs.DefaultMaterialID);
var cubeMaterial = this.Managers.AssetSceneManager.Load<Material>(EvergineContent.CrateMat);
float sliderLength = 3;
// Create the slider holder...
Entity slider = new Entity()
.AddComponent(new Transform3D()
{
Scale = new Vector3(sliderLength, 0.1f, 0.1f),
Rotation = new Vector3(0, 0, MathHelper.ToRadians(-10)) // Rotate the slider axis by 10º
})
.AddComponent(new MaterialComponent() { Material = material })
.AddComponent(new CubeMesh())
.AddComponent(new MeshRenderer())
.AddComponent(new RigidBody3D()
{
PhysicBodyType = RigidBodyType3D.Kinematic
});
// Create the sliding object...
Entity cube = new Entity()
.AddComponent(new Transform3D())
.AddComponent(new MaterialComponent() { Material = cubeMaterial })
.AddComponent(new CubeMesh() { Size = 0.5f })
.AddComponent(new MeshRenderer())
.AddComponent(new RigidBody3D()
{
PhysicBodyType = RigidBodyType3D.Dynamic,
});
// Create the Joint
slider.AddComponent(new Generic6DofJoint3D()
{
ConnectedEntityPath = cube.EntityPath,
UseLinearLimit = true, // Limit the slider
LowerLinearLimit = new Vector3(0, 0, -sliderLength / 2),
UpperLinearLimit = new Vector3(0, 0, sliderLength / 2),
});
this.Managers.EntityManager.Add(slider);
this.Managers.EntityManager.Add(cube);
}