Lights

Evergine uses an advanced lighting model to simulate how light affects geometries. It also supports multiple lights in the scene, allowing a wide range of environments and possibilities.
Every type of light is modeled in Evergine using a Light component.
Create a Light in Evergine Studio
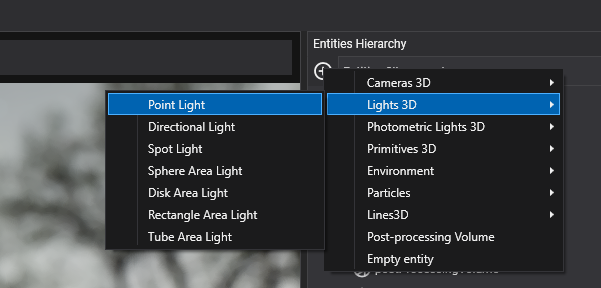
In the Entities Hierarchy panel of your Scene Editor, click "Add Entity," select Light, and then choose the kind of light you want to create:
- Point Light
- Directional Light
- Sphere Area Light
- Spot Light
- Disc Area Light
- Rectangle Area Light
- Tube Area Light
We discuss the light types later in this article.
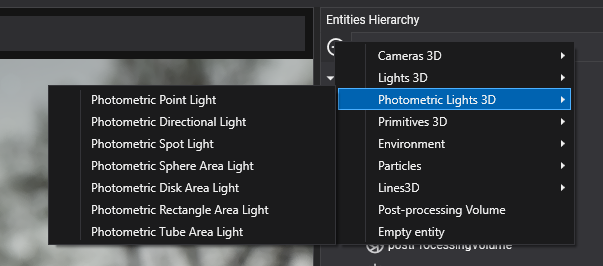
Additionally, we can create photometric lights from the same panel with these options:
- Photometric Point Light
- Photometric Directional Light
- Photometric Sphere Area Light
- Photometric Spot Light
- Photometric Disc Area Light
- Photometric Rectangle Area Light
- Photometric Tube Area Light
Create Light from Code
The following sample code can be used to instantiate a new basic point light entity in a scene.
protected override void CreateScene()
{
// Create a new light entity.
Entity pointLightEntity = new Entity()
.AddComponent(new Transform3D())
.AddComponent(new PointLight()
{
Color = Color.Red,
Intensity = 3,
LightRange = 10
});
// Add the light entity to the entity manager.
this.Managers.EntityManager.Add(pointLightEntity);
}
Basic Light Properties
These are the basic properties that almost all lights have.
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| Is Enabled | If the light is on/off. |
| Shadow Enabled | Enable/disable shadow mapping for this light. |
Photometric / Non-Photometric Lights
Photometric lights use photometric (lighting units) allowing you to define lights as they would be in the real world. They are configured using physical parameters. Evergine supports both photometric and non-photometric lights, and it offers the same light types duplicated based on this choice.
Common Photometric Properties
Every photometric light (no matter what type it is) defines these parameters. Additionally, each specific type of light defines its own intensity unit properties.
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| Color By Temperature | Indicates if the light color will be overridden using the light temperature. |
| Temperature | The light temperature in Kelvin (K). When ColorByTemperature is true, the light color is overridden by the light temperature. |
Note
Light intensity unit depends on the light type (for example, PointLights are measured in Lumens, whereas DirectionalLights are measured in Lux).
Non-Photometric Light Properties
On the contrary, if you create regular lights, you can use the basic light properties:
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| Color | The RGB color tint of the light. |
| Intensity | The light intensity value in a non-standard unit. Greater values will produce brighter illumination. |
Types of Lights
There are different types of lights, each useful for a different scenario. In general terms, lights are divided into two general categories:
- Directional Lights: These lights have unlimited boundaries, and every object is affected by this light type.
- Volume Lights: The light influence is delimited by a range.
- Area Lights: A subtype of volume lights that emulate lights coming from an area instead of a point in space.
Directional Lights / Photometric Directional Light
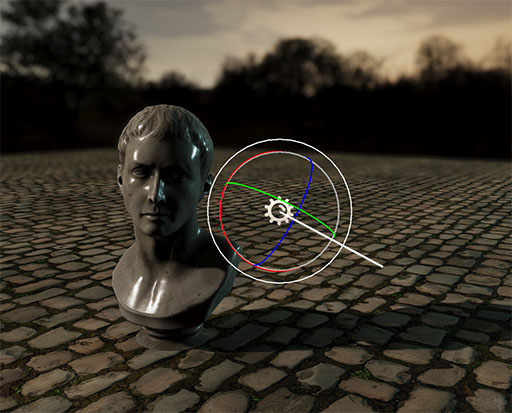

Directional lights are lights that come uniformly from one direction and at an infinite distance. They're used to simulate distant light sources like the sun. They use the forward vector of their entity's Transform3D for calculating the light direction.
In the case of using a Photometric Directional Light, the intensity is measured using the following property:
| Photometric Property | Description |
|---|---|
| Illuminance (Lux) | The light illuminance measured in Lux. Indicates the total luminous flux incident on a surface, per unit area. |
Volume Lights
Volume lights are a common type of light in which the light source comes from a specific point in space, and its intensity decays with distance.
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| Light Range | The light range in meters. |
In the case of using Volume Photometric Lights, the intensity is measured using the following property:
| Photometric Property | Description |
|---|---|
| Luminous Power (Lumen) | The light luminous flux in Lumen. |
Point Light / Photometric Point Light
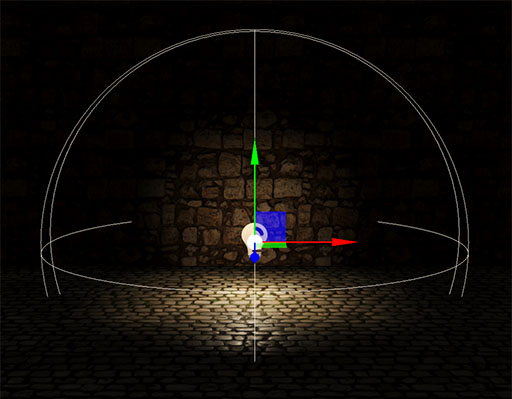
A point light is located at a point in space and emits light equally in all directions within its sphere range. Its intensity decays with distance from the light, reaching zero at its maximum range. It's useful for local lights like lamps.
Spot Light / Photometric Spot Light
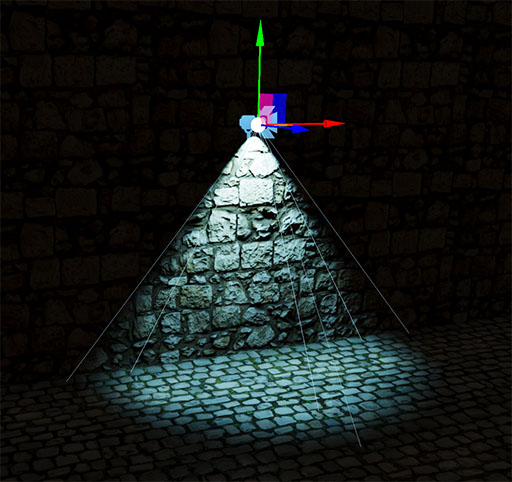

A spot light is also placed in a specific location and has a range over which the light decays. However, spot lights are constrained by an angle, defining a cone-shaped light.
Specific Properties
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| InnerConeAngle | The inner angle of the spotlight cone. |
| OuterConeAngle | The outer angle of the spotlight cone. |
Tube Area Lights / Photometric Tube Area Light

Tube Area Lights are lights that come from a line segment and have a range and emission thickness. They are useful for simulating neon lights.
Specific Properties
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| Length | The length of the tube light volume. |
| Radius | The radius of the tube light volume. |
Sphere Area Lights / Photometric Sphere Area Light

Sphere Area Lights behave like a physical sphere emitting light rather than a point light. They create much softer lighting and can be used for creating dynamic environments.
Specific Properties
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| Radius | The radius of the sphere light volume. |
Disc Area Lights / Photometric Disc Area Light
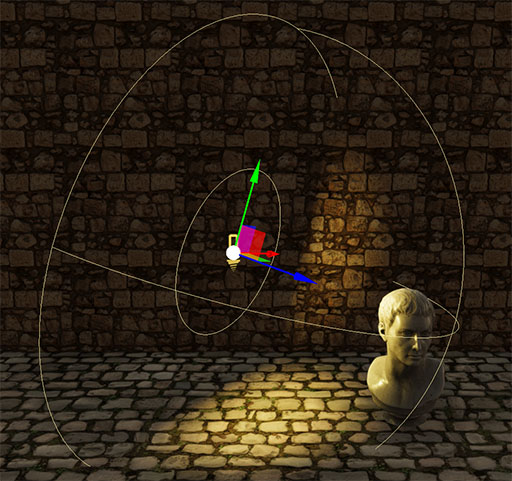

Disc Area Lights emit their light from a disc with a specified radius and a maximum range. Useful for creating artificial soft lights.
Specific Properties
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| Radius | The radius of the disc area light. |
Rectangle Area Lights / Photometric Rectangle Area Light
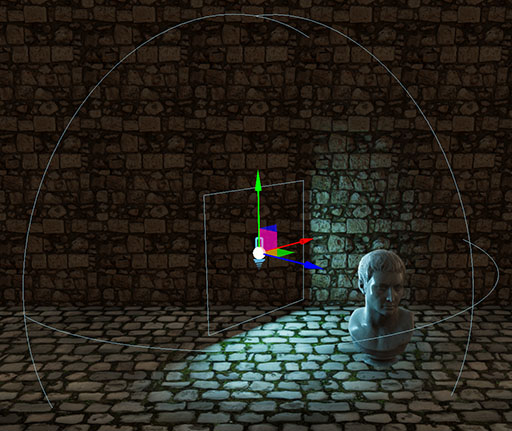

Rectangle Area Lights emit their light from a rectangle with a specified width and height, at a maximum range. Useful for creating indoor window lighting, for example.
Specific Properties
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| Width | The width of the rectangle area light. |
| Height | The height of the rectangle area light. |
Note
Area lights need to make complex calculations to properly simulate their shape. Therefore, they are significantly more performance-heavy than their punctual counterparts (Point, Spot, and Directional).
Shadows
To enable light cast shadows, the following properties have been added:
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| Shadow Enabled | Enable/disable shadow mapping for this light. |
| Debug Mode | Debug ShadowMap cascades used to generate this light shadow. |
| Shadow Opacity | Value [0-1] that represents the total opacity of the shadow. 1 by default. |
| Shadow Bias | Shadow bias for this specific light. Choosing the correct bias value allows control over shadows artifacts like a Moiré-like pattern or Peter panning. |